- Sep 7, 2024
How Seasonality Impacts the Stock Market
- Brian Montes
- 0 comments
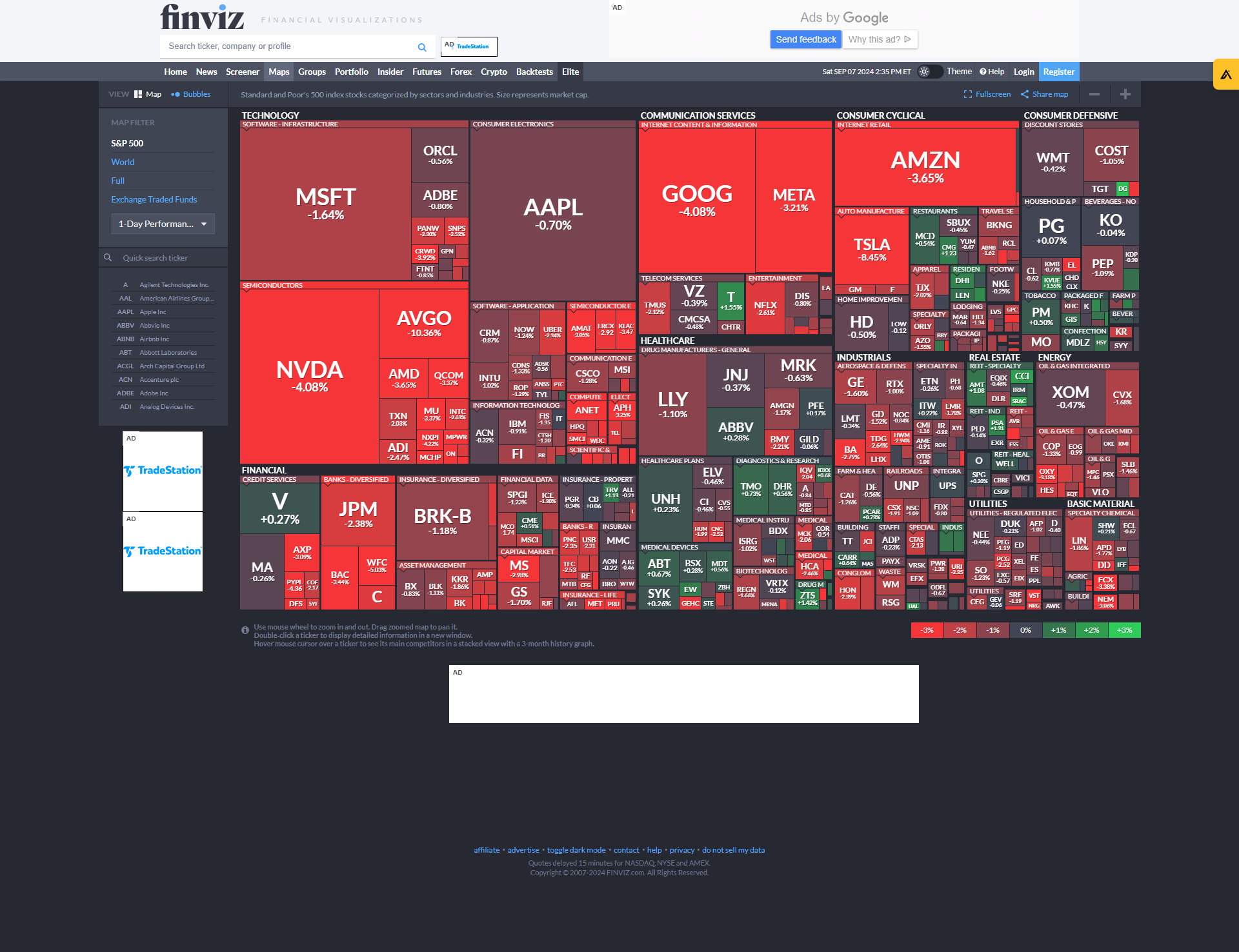
September 2024 lived up to its reputation as the worst month historically, kicking off with a sharp sell-off. We finished August with 90% of stocks trading above their 20-day moving average, usually a sign that the rally was likely running out of steam. As often the case, failure to break above previous highs spelled trouble for the markets and left us vulnerable to a pullback.
What now? We must defer to the trend, as short-term momentum has shifted negatively. Until the S&P 500 recovers critical resistance levels, starting with 5,500, we must remain cautious and watch for further downside. And a retest of the August 2024 lows can't be ruled out just yet.
Understanding seasonality in the stock market can be a game changer for traders, especially swing traders looking to time their trades more effectively. Like seasons, the stock market has cycles driven by various factors such as business activity, investor behavior, and weather. Recognizing these patterns can give traders a strategic advantage, helping them navigate the market confidently. With that said chart analysis should still be your primary decision-making tool. Never assume seasonality will happen just because it has happened in the past.
In this post, we’ll explore seasonality, key seasonal trends to watch, how different sectors are affected, and how swing traders can use this information to improve their results.
What is Seasonality in the Stock Market?
Seasonality refers to recurring patterns that occur in the stock market at specific times of the year. Historical trends, investor behavior, and economic cycles drive these patterns. While seasonality is not a guaranteed predictor of market performance, it provides valuable insights that traders can incorporate into their decision-making.
Knowing when specific sectors or stocks tend to perform well—or poorly—can help swing traders better plan their entries and exits. However, it’s crucial to remember that seasonality should be combined with other forms of analysis for the best results.
Key Seasonal Trends in the Stock Market
1. The January Effect
The January Effect refers to the tendency for stocks, particularly small-cap stocks, to rise in January. This happens because many investors sell off losing stocks in December to capture tax losses, then repurchase them in January, creating upward pressure on prices. For swing traders, January can present opportunities to capitalize on this early-year momentum.
2. Sell in May and Go Away
The adage "Sell in May and go away" is based on the observation that the market often underperforms from May to October. Summer months generally see lower market volume as many institutional investors and traders take vacations, leading to reduced liquidity and sometimes greater volatility.
As a swing trader, being cautious during this period is essential. While not a hard-and-fast rule, you may find fewer favorable setups or need to adjust your strategy for more choppy, unpredictable price movements.
3. Back-to-School Rally and Q4 Momentum
Market activity typically picks up in September as traders return from summer breaks. The fourth quarter is also significant, with many companies preparing for year-end earnings reports. This time of year includes the "Santa Claus Rally," a tendency for stocks to rise during the last week of December and into the first days of January, driven by investor optimism for the new year.
4. Earnings Seasons
Earnings season occurs four times a year when companies report quarterly results. These periods can create significant price movements as traders react to earnings beats or misses. Understanding how seasonality aligns with earnings releases can provide valuable context for trading decisions.
Sector-Specific Seasonality
Different sectors of the stock market are affected by seasonality in unique ways. For example:
- Retail and Consumer Goods: These stocks often perform well in the months leading up to the holidays as consumer spending increases.
- Energy Stocks: Energy companies tend to see increased demand for heating fuels and oil during colder months.
- Technology Stocks: The fourth quarter is typically strong for tech companies, as holiday spending boosts gadgets and consumer electronics sales.
By considering these sector trends, swing traders can better time their trades and allocate capital to the right areas at the right times.
The Psychological Aspect of Seasonality
Investor psychology plays a significant role in seasonality. For example, during the summer, lower market participation and investor disengagement can create volatility. Conversely, as people refocus on their financial goals after the summer, increased market participation drives more muscular market activity in the fall.
Recognizing these psychological patterns can help traders avoid emotional trading decisions and capitalize on other investors' collective behavior.
How Swing Traders Can Use Seasonality
Now that you understand the concept of seasonality, here are some practical tips for integrating it into your swing trading strategy:
1. Combine Seasonality with Other Indicators: Don’t rely solely on seasonal patterns. Use technical indicators such as moving averages or MACD to confirm trades, ensuring that you’re trading in line with market conditions and historical trends.
2. Plan Around Earnings Seasons: Be aware of when the stocks you’re trading are due to report earnings. Earnings releases can either support or disrupt seasonal trends, so factoring them into your strategy is essential.
3. Adjust Position Sizes: During historically volatile times like October or earnings seasons, you might want to adjust your position sizes or set tighter stop losses to protect your capital.
4. Stay Flexible: While seasonality can provide valuable insights, the stock market is only partially predictable. Stay agile and be ready to adjust your strategy if the market moves unexpectedly.
Conclusion
Seasonality in the stock market is a valuable tool for traders, especially swing traders looking to time their trades more effectively. You can make better-informed trading decisions by understanding how the market tends to behave during specific times of the year—and how this impacts different sectors. Just remember, seasonality works best when used alongside technical and fundamental analysis.
Incorporating seasonality into your trading approach can provide you with a broader perspective, helping you navigate the market’s cycles with greater precision. Happy trading!